The C3 carbon bridge
One of C3’s core pieces of infrastructure is its automated carbon bridging technology. This infrastructure allows a carbon credit to be bridged onto the blockchain by collecting its key metadata and creating a one-for-one copy of it on the blockchain as a “tokenized carbon credit”. Most often, this process is completed with a batch of more than one carbon credit.
A reminder that in our last blog we covered some key concepts and terms for carbon credits themselves and why they are such an important tool to address our growing, global carbon footprint.
Why do we need carbon bridges?
Companies across the world are moving to the Web3 space to explore innovative means of building client relationships, building efficiencies into their digital systems, and leveraging the power of blockchain to bring security to their data.
The Voluntary Carbon Market (VCM) is one area that has seen considerable Web3 interest in the past year. As of July 2022, over 25,000,000 tonnes of carbon offsets have migrated from traditional carbon registries to the Polygon blockchain that C3 and other leading tokenized carbon market players call home. There is a clear advantage to using the blockchain for the VCM — it delivers clear price transparency for buyers, programmatic purchases & offset retirements, and deep liquidity for individuals and businesses to source from.
In 2021, the Voluntary Carbon Market surpassed $1billion in traded value. The market is expected to more than double by 2027. Although the expected growth rate of the market is significant (although not unprecedented, and not in line with the Taskforce on Scaling the Voluntary Carbon Market’s projections of what is required to close the emissions gap), there are a number of issues that mar the market’s ability to scale-up, including:
- Poor liquidity which inhibits market efficiency and deal flows
- Poor transparency around market operations and ethics
- A lack of data to help market participants make informed decisions.
By working directly with carbon offset Standards and Registries, C3 seeks to overcome these barriers, and support the market to scale significantly with sustained corporate demand and novel areas of demand emerging (such as those offered by Web3 projects).
C3 acts in synergy with the wider on-chain VCM, where C3 enables high quality carbon offsets to integrate with on-chain markets such as KlimaDAO’s by providing guidance and technical support to registries who wish to onboard credits into this ecosystem. In addition, C3 aims to increase adoption of these markets for conventional sources of demand (such as corporate offsetters) who wish to receive the benefits of using them.
How does it work?
Tokenized carbon credits are those which have been transferred onto the blockchain, typically into the form of an ERC-20 token; they are fungible tokens on the Ethereum network. They represent a pooled group of similar (e.g. technology type; vintage; region) carbon credits that have been bundled into an index.
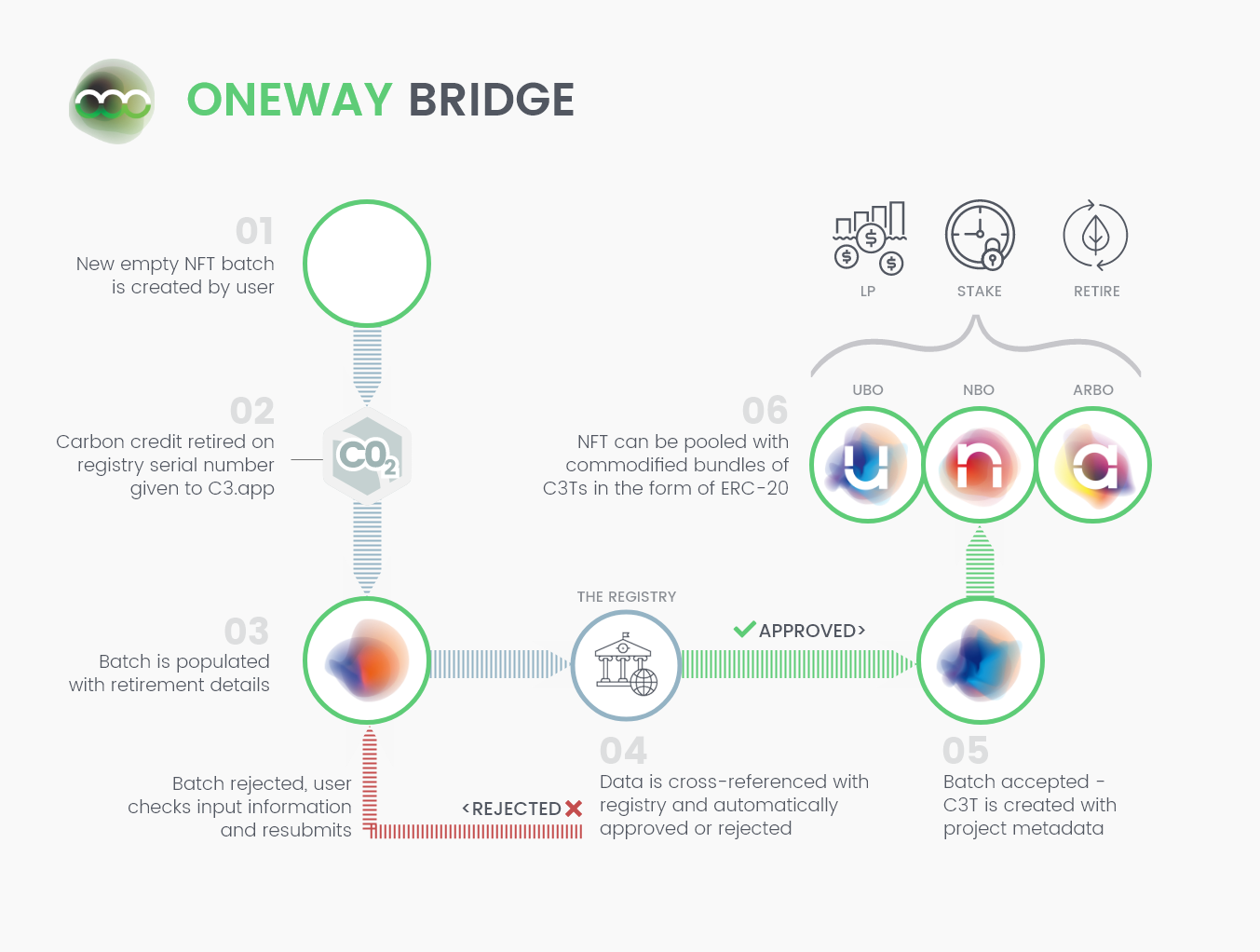
The process for creating tokenized carbon starts by using a carbon bridge such as C3’s. The bridge takes carbon credits that are specially retired for the purpose of tokenization and first converts them into a C3T token. The C3T token is an ERC-721 token (also referred to as a non-fungible token or an NFT), which holds a set of unique data, including a unique serial number which corresponds to the registry’s retirement details for a given batch of carbon credits. Once the C3T is created, the NFTs can then be ‘pooled’ with like-for-like counterparts into the fungible ERC-20.
Key characteristics of the carbon offsets are brought on-chain when it is transformed into a TCO2, including:
- Project Name
- Serial Number
- Project type (renewable energy, forest carbon project, blue carbon, etc.)
- Vintage Year
- Verification Standard
- Retirement hash
When a user wishes to ‘retire’ a number of tokenized carbon credits — the ERC-20 token can be used to redeem the underlying ERC-721. The ERC-721 can be retired by writing this action onto the blockchain and removing the token from the market. This gives the user a permanent record on the blockchain which demonstrates the time, volume and type of tokenized carbon retired.
This bridging process is referred to as ‘one way’ bridging. This means that because the carbon credit is retired prior to it being migrated onto the blockchain, it cannot ever be traded in the legacy system again. This removes the double-counting risk of the carbon credit and is analogous to the process undertaken when e.g. converting and transferring CDM certified carbon credits from their native registry to Verra’s registry as VCUs.
Below is an infographic describing the one way bridge process.
How might carbon bridges innovate?
The on-chain carbon market launched in Autumn 2021, it is by all accounts a new area of innovation. As the sector matures, there will be new technologies developed to meet the evolving needs of market stakeholders. For example, the Verra carbon registry has recently announced a consultation on their framework for tokenized carbon.
C3 has been working to define new approaches that could unlock additional benefits for the market, one of these is the development of a two-way bridging technology. Two-way bridging technology is similar to that of one-way bridging, in that it gives carbon credits presence on the blockchain in a tokenized (ERC-20) state. However, in the case of two-way bridging, the tokenized carbon credits can be redeemed for unretired, untokenized carbon credits after they have been tokenized.
To achieve this, the carbon credits themselves must be kept as ‘live’. This can be achieved through the utilization of a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) that takes custody over carbon credits that holders wish to tokenize; when the credits are under custody, a tokenized credit can be issued onto the blockchain and used within the on-chain ecosystem.
If that tokenized carbon credit is not used on-chain (i.e. it is not retired), it could subsequently be unwrapped and then redistributed to the owner of the credit. Thus enabling greater integration of the on-chain and off-chain carbon market.
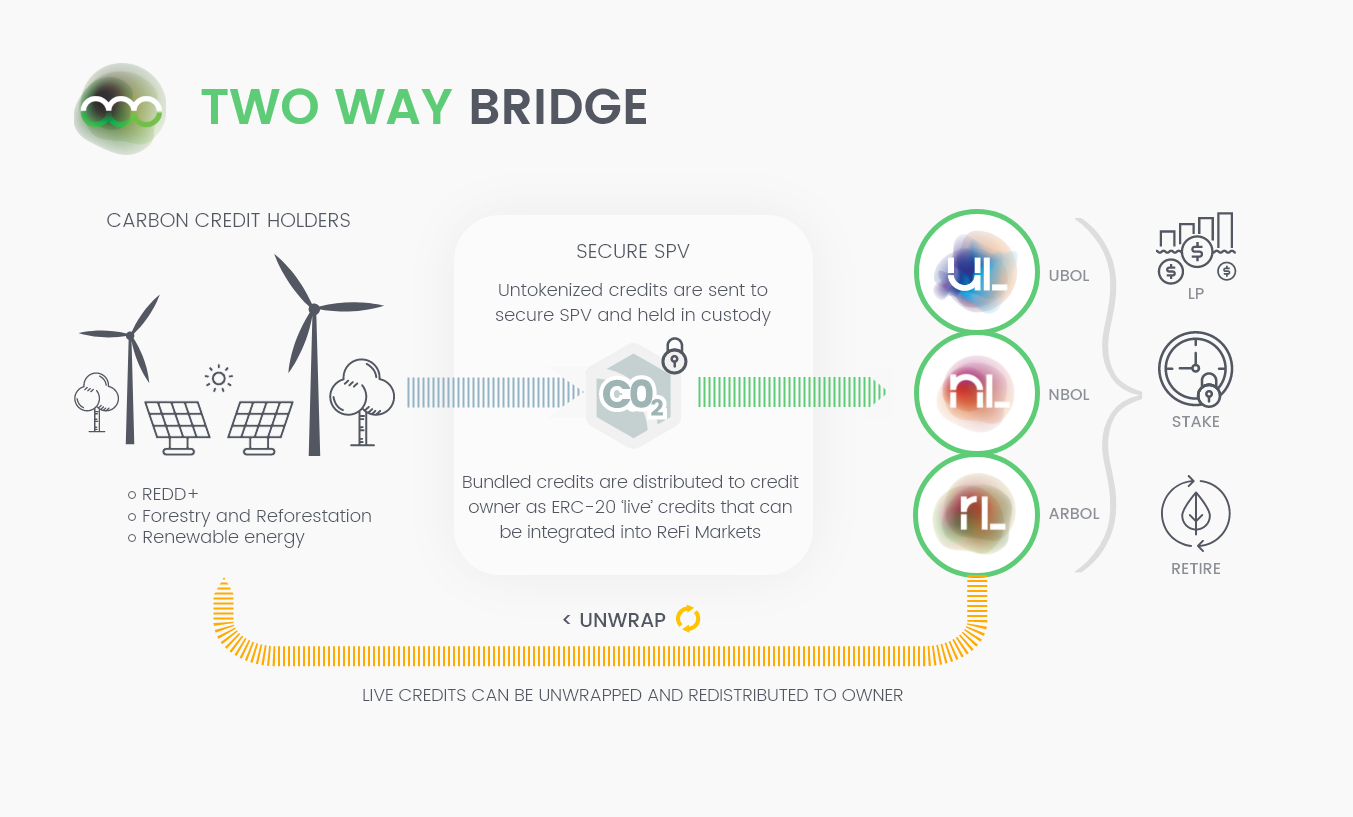
C3’s objective is to maximize the bandwidth between the legacy carbon markets and the blockchain-enabled carbon markets. To do this, we use cutting edge technology developed by our team which leverages Web3 to deliver benefits for the whole market.



